CT examination of the small intestine can reveal areas of narrowing, bowel wall swelling, and thickening. The examination also allows assessment of structures outside the intestine, such as the mesentery, abdominal lymph nodes, and internal organs.
Computed tomography (CT) examination of the small intestine
The most common indications for a CT examination of the small intestine are suspected inflammatory changes or tumors in the small intestine.
Check the patient instructions you received for specific preparation guidelines. You may need to follow a special diet, empty your bowels, and fast before the examination.
An iodine-based contrast agent may be administered intravenously during the examination, so you will be asked about any allergies. If you have a known allergy to iodine-based contrast agents, inform the referring physician when scheduling the examination and notify the radiographer upon arrival.
If you know or suspect that you are pregnant, inform your treating physician or at the latest when arriving for the examination. CT are generally avoided during pregnancy.
Before the examination, you will be asked to drink a contrast solution over a 45-minute period, which you will receive from the radiology department. This solution does not contain iodine. Its purpose is to fill the entire small intestine.
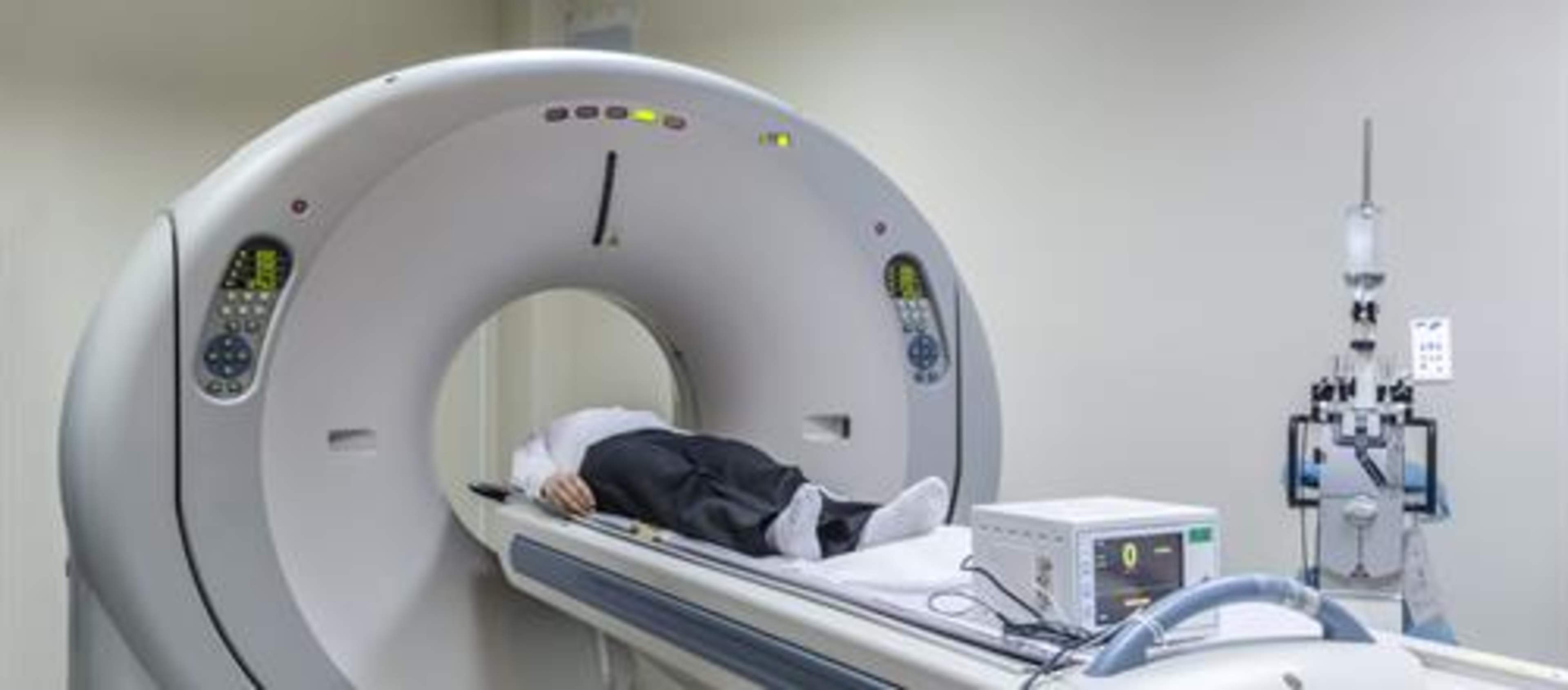
You will lie still on the examination table, which moves slowly through the scanner ring during imaging. For abdominal examinations, you may be asked to hold your breath to prevent motion artifacts. The itself is very quick, and each breath-hold is brief. The intravenous contrast agent may cause a temporary sensation of warmth and a mild metallic taste in the mouth.
The actual imaging takes 5–15 minutes, but the preparation, including drinking the contrast solution, adds approximately one hour to the total examination time.
CT examination generally do not require follow-up and do not restrict normal activities. If contrast agent was used, you will be advised to drink plenty of water. This helps flush the contrast agent from your body through urine within a few hours.
If contrast agent is used, you may be asked to wit for a short time after the imaging to monitor for any allergic reactions. Contrast agents are typically safe. The oral contrast solution may cause temporary diarrhea.
A radiologist will review and interpret the images and write a report. The physician who referred you for the examination will inform you of the results and the next steps in your care. Contact your care unit if you do not have a scheduled appointment or call time.
CT examination is a fast, painless, and safe diagnostic method. If contrast agent is used, there is a small risk of allergic reaction. In such cases, your condition will be monitored after the imaging. Reactions can be prevented and treated with medication.
CT examinations use X-ray radiation. The amount of radiation depends on the scope of the examination.
The radiation dose from a CT examination and the associated risk is low. If you have concerns about radiation, you can ask your treating physician or radiology staff for more information. You can also find details about radiation exposure and doses from different examinations in the Information about radiation section.
Updated 21.10.2025

