Bone density test is used to determine whether there is osteoporosis or a pre-stage of it in the skeleton. It is a reliable method for assessing bone strength and the fracture risk caused by osteoporosis. The examination uses X-rays and is therefore not suitable for pregnant women.
Bone densitometry
Bone density test is used to assess bone density through X-ray imaging. The examination can be performed on both adults and children.
Upon arrival, you will be asked for your height and weight. No other preparations are required. However, please read the patient instructions you have received carefully.
The radiographer will instruct which clothing items containing metal (i.e. jeans, bras) and jewelry must be removed for the duration of the examination.
If you know or suspect that you are pregnant, inform your treating physician or at the latest when arriving for the examination. The physician and, if necessary, the radiologist will decide on a suitable imaging method for you.
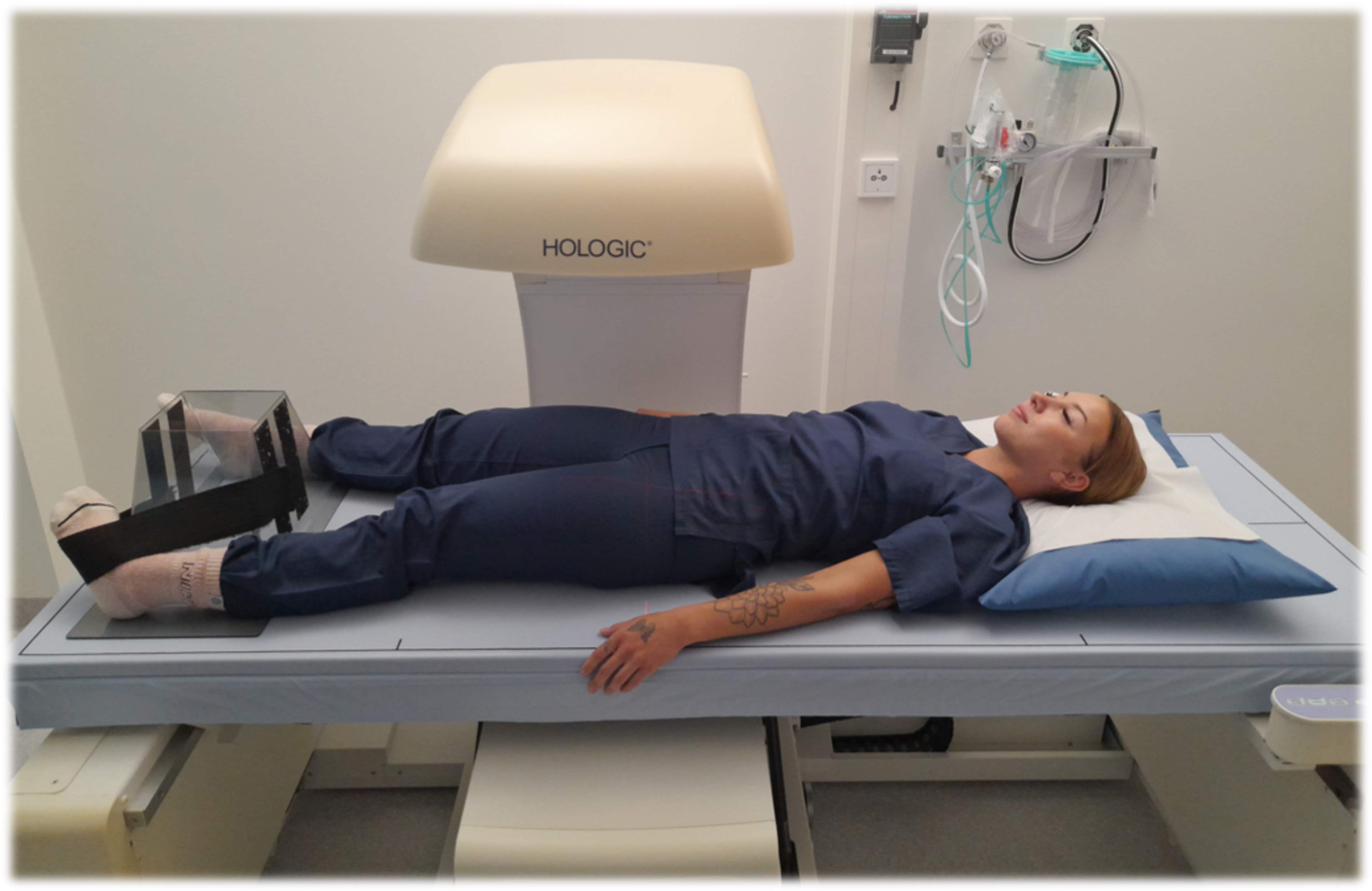
During the examination, you will lie on your back on the imaging table. The examination is quick, and it is important to remain still during it. The examination is painless.
While the examination is being performed, the radiographer will be in the same room to monitor its success.
Bone density can be measured from the whole body, lumbar spine, hip, or wrist. The entire examination usually takes 15–30 minutes.
Bone density test does not require follow-up and does not impose restrictions on normal daily activities.
The radiologist will provide a report on the examination. The physician who referred you for the examination will inform you of the results and discuss further treatment. Contact your care unit if you do not have a scheduled appointment or call time.
Bone density test is a quick, painless, and safe examination method. It is performed using low-dose X-ray radiation and is therefore not suitable for pregnant women.
The final radiation dose depends on the technique used and the number of images taken. The radiation dose from an X-ray examination and the potential risk from radiation is small.
If you have concerns about radiation, you can always ask for more information from your treating physician or the radiology staff. Information about the effects of radiation and the radiation doses of different examinations can also be found in our Information about radiation section.
Updated 27.11.2025

