Laboratory examinations
All pregnant women undergo blood type and antibody testing during pregnancy. The screening, performed from a blood sample taken in early pregnancy, aims to identify mothers whose babies are at risk of developing hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn—a condition where the red blood cells of the fetus or newborn break down.
The sample is taken from all mothers who attend maternity clinics during pregnancy weeks 8–12. Additional samples may be taken later in pregnancy if necessary.
Almost all pregnant women also undergo a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test during pregnancy. This test can detect gestational diabetes. The maternity clinic provides a referral and instructions for the laboratory test. The test involves taking a fasting blood glucose sample after a 12-hour fast, followed by drinking a solution containing 75 grams of glucose. Blood glucose samples are then taken 1 and 2 hours after drinking the solution.
Laboratory examinations during pregnancy can generally be performed without restrictions.
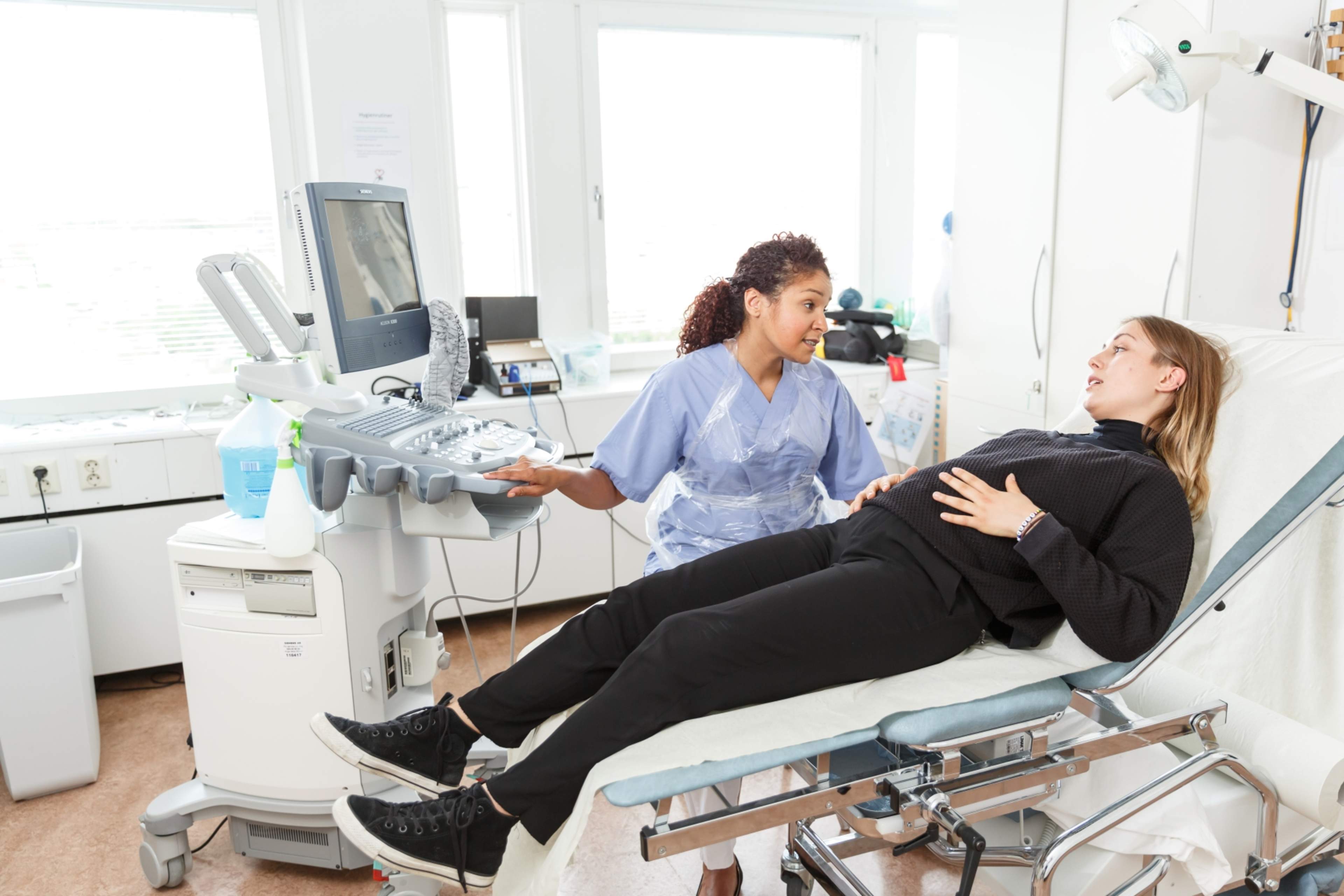
Imaging examinations
If you know or suspect that you are pregnant, inform your treating physician or at the latest when arriving for imaging examination. The referring physician and, if necessary, the radiologist responsible for the imaging will determine the appropriate imaging method for you.
Ultrasound examinations can be performed during pregnancy. Routine pregnancy monitoring ultrasounds are conducted at maternity clinics.
Pregnancy does not prevent X-ray imaging outside the abdominal area, as the radiation dose to the fetus is negligible in such cases.
If the X-ray or computed tomography (CT) examination targets the abdominal or pelvic area, the radiologist responsible for the imaging will always assess the situation individually. In such cases, alternative imaging methods are usually preferred when possible. If you are scheduled for an abdominal or pelvic X-ray or CT examination, please ensure that the healthcare staff is aware of your pregnancy before the examination.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be performed at any stage of pregnancy if the mother's condition requires it. MRI is generally avoided during early pregnancy as a precaution if the condition being examined can be safely postponed.
The use of MRI contrast agents is not recommended during pregnancy, but exceptions may be considered if necessary due to the mother's condition. During breastfeeding, there are no restrictions on the use of contrast agents.
Isotope and PET examinations are only performed on pregnant women in exceptional cases.
If you have concerns about undergoing an examination, you can always ask for more information from your treating physician or the staff of the imaging unit performing the examination.