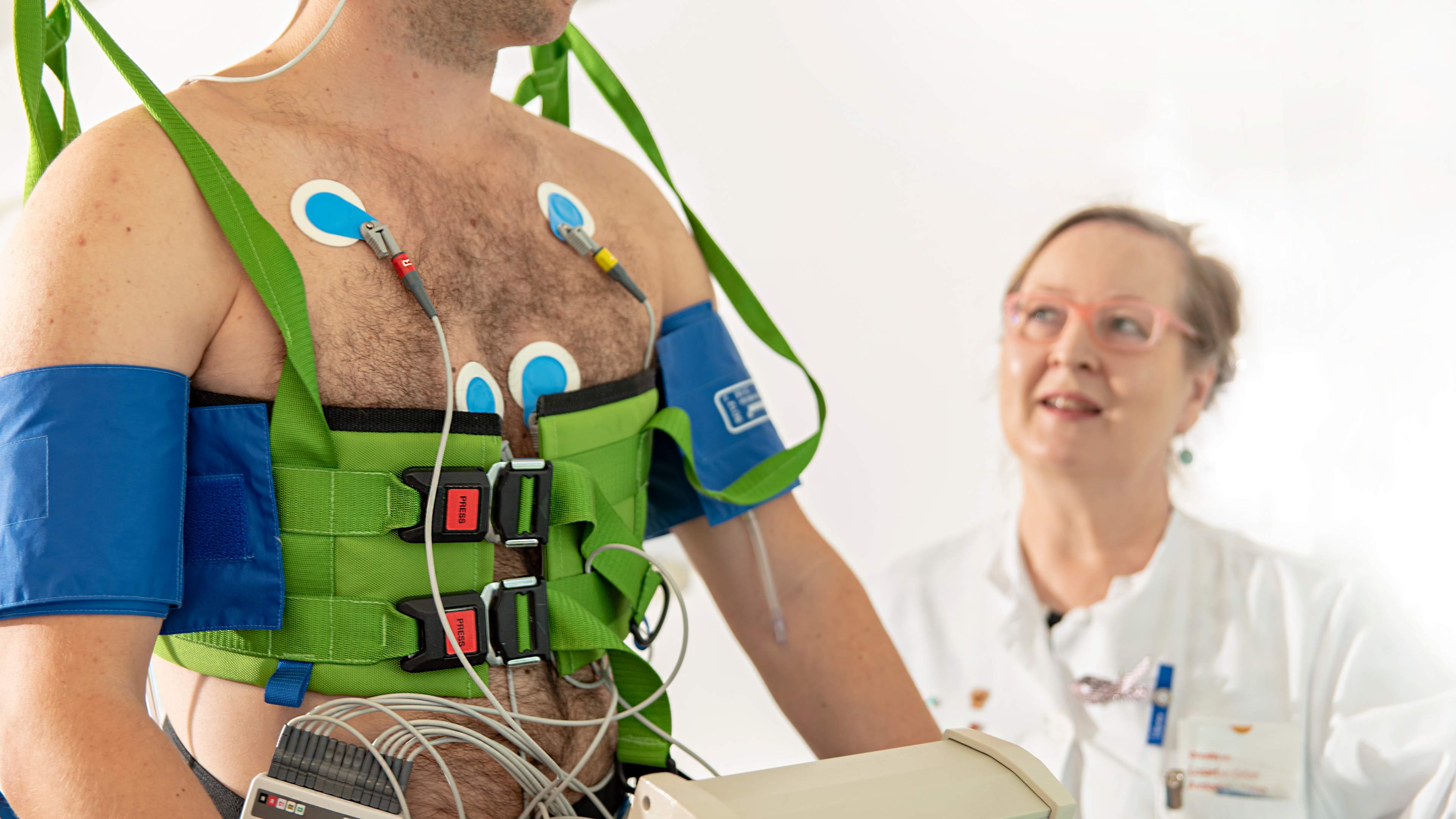
Depending on the type of examinatio and the clinical situation, a stationary bicycle, treadmill, or arm crank may be used.
Types of exercise stress tests include:
Clinical exercise stress test
Spiroergometry
Blood flow measurement in lower limb arteries during exercise (ABI stress test)
Stress echocardiography
During the test, blood pressure and ECG (electrocardiogram) are monitored. Measurements may be taken before, during, and after exertion. The workload is increased gradually. The examination is always conducted under supervised conditions, and a physician is present throughout. The unit performing the examination will provide detailed instructions for preparation.
Watch the video: Exercise stress tests. The video is produced by HUS and includes subtitles in Finnish, Swedish, and English.