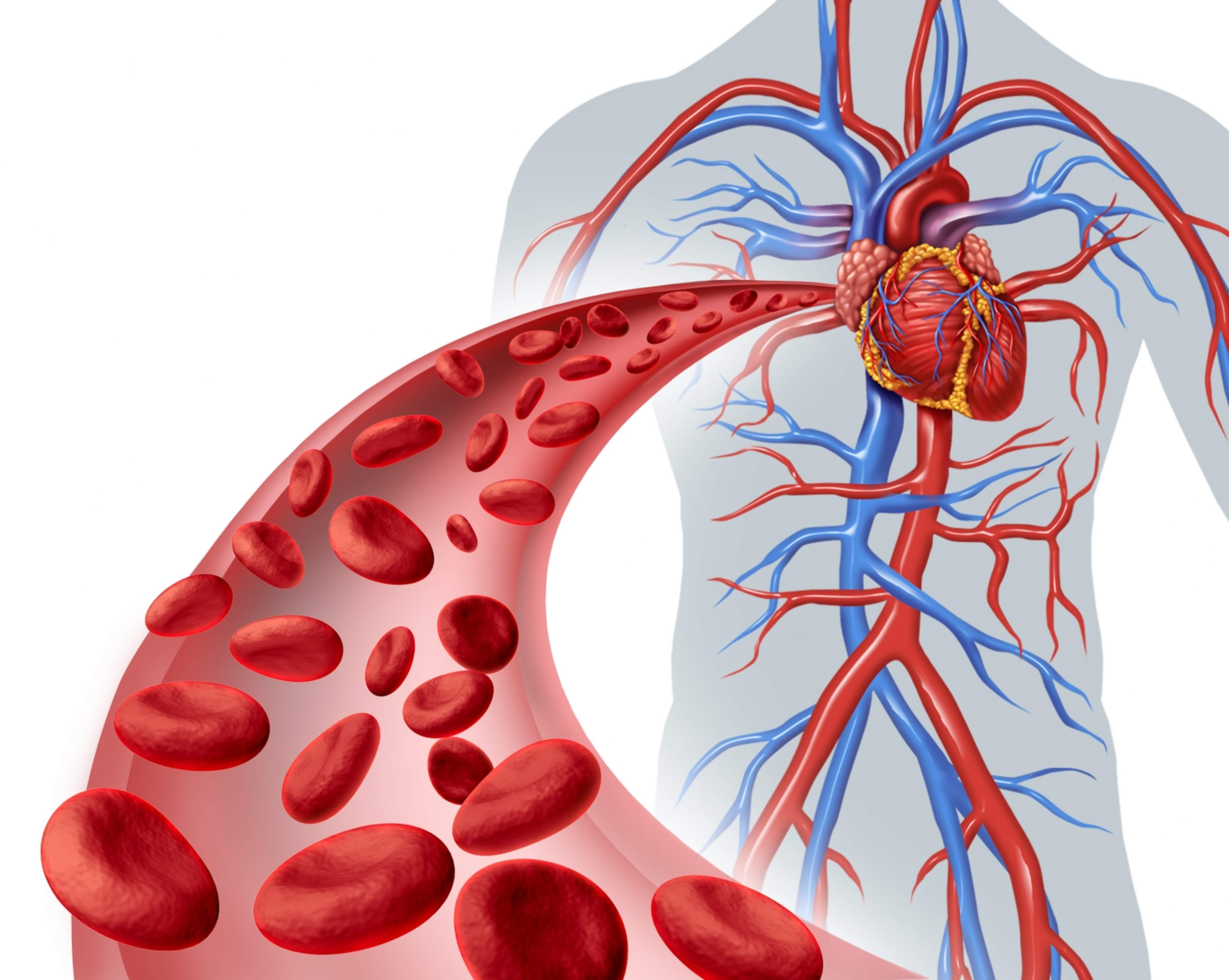
Arterial disease (atherosclerosis) is a condition where blood-transporting arteries become narrowed, disrupting the flow of blood through the artery. A popular expression for the disease is “artery calcification,” even though the contraction is not calcareous by nature. It is the build-up of fats on the artery walls caused by acidified LDL cholesterol as well as an inflammation. In a person with diabetes, the build-up of fat occurs more easily.
Due to the high risk of arterial disease, the proper treatment of diabetes includes not only the treatment of blood sugar but also non-smoking, a healthy diet, exercise and, if necessary, the medication of high cholesterol and hypertension. The risk factors of arterial disease are always mapped when diabetes is first diagnosed and then in connection with the annual check-ups.
With the proper treatment of diabetes and arterial disease risk factors, the incidence of and mortality from arterial diseases have been reduced in people with diabetes as well as others.
Find out your own arterial disease risk factors and set your personal goals:
What was your LDL cholesterol level in the blood test?
Is your blood pressure at the target level?
Do you smoke?
What is your long-term blood sugar balance like: what is your HbA1c result?
Talk to your doctor or nurse about the treatment and the changes you need to make to your lifestyle, if you haven’t reached your target yet.

